Latest Update
Blogs
December 3,2019
/ adminAll You Need to Know About Pediatric Cirrhosis
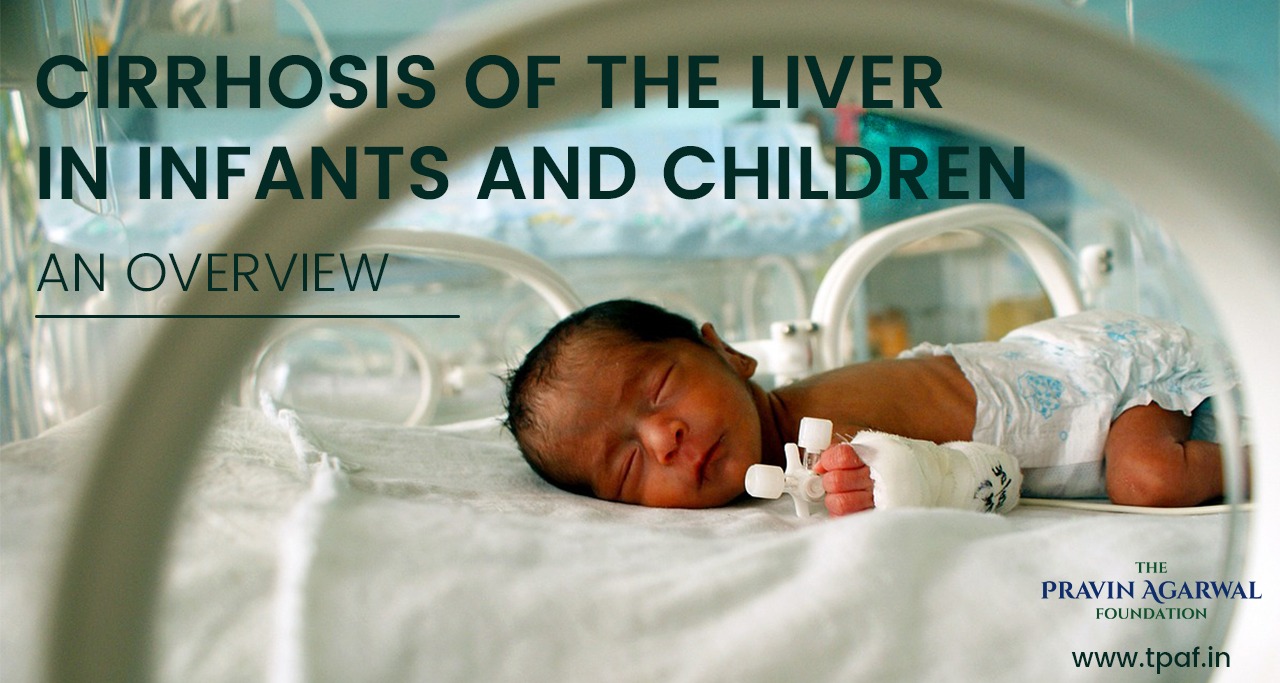
The liver is one of the largest and most vital organs of the human body that is easy to overlook until something goes wrong. Everyone has a liver, but nobody thinks about it. Like heart, the liver does not pound when it feels nervous or does not make growling noises like stomach when getting hungry. The liver is a very determined organ that keeps working even when the two-third part of its damage. That is why, until when it is healthy, it is easy to ignore it. Although the liver always works behind the scene, when it stops working, it can lead to death.
Here, in this blog, we will discuss cirrhosis in children, its symptoms and causes, and treatment. However, before diving deep into it, let us first understand what pediatric cirrhosis is.
What Is Cirrhosis of the Liver in Children?
Cirrhosis of the liver in children is a progressive pediatric liver disease in which scar tissue replaces soft and healthy liver tissue. As soon as scar tissue is starting to buildup, the liver becomes hard. Then slowly, it cuts off blood circulation in the liver. It interferes with the liver’s many vital functions incorporating the liver’s capability to process nutrients and filter toxins.
In life-threatening cases, the liver stops working, and the only option left is a pediatric liver transplant.
Signs and Symptoms of Pediatric Cirrhosis
Most of the time, in the early stage, cirrhosis does not produce any symptoms. However, as cirrhosis progresses, a child may have the following symptoms.
- nausea or vomiting
- weakness
- loss of appetite
- abdominal pain or swelling
- spider-like blood vessels on the skin
- weight loss or trouble gaining weight
With time, cirrhosis can lead to the following serious issues.
- Jaundice
- Bleeding easily or blood loss
- swelling of the legs or abdomen from built-up fluid
- Difficulty in thinking or confusion (encephalopathy). It occurs because of the accumulation of waste products from food in the bloodstream.
In cirrhosis, blood cannot flow flawlessly through a liver, so the pressure in the portal vein may increase. This condition is called portal hypertension. It causes its symptoms and complications, such as hepatopulmonary syndrome. It is a rare condition that affects the lung’s ability to supply oxygen to the rest of the body.
If a child does not receive proper treatment of cirrhosis, it can lead to the following serious complications.
- kidney failure
- diabetes
- liver cancer
- malnutrition
What are the causes of Pediatric Cirrhosis?
The liver itself has an excellent capability to heal itself, but a long-term illness or injury can scar the liver. Let us check out the following conditions that can cause cirrhosis in children.
- Fatty liver disease
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Some inherited heart defects
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
- Wilson disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Biliary atresia
- Exposure to certain medications and toxins incorporating high levels of vitamin A and drug used to treat cancer.
- Bile duct diseases
- Cystic fibrosis
- Tyrosinemia
How is cirrhosis of the liver analyzed and assessed?
If the doctor suspects pediatric cirrhosis, he/she may suggest performing one or more the following imaging tests.
- Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan – It helps to determine the severity of cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
- Abdominal ultrasound–This test allows the evaluation of blood flow to and from the liver.
- Elastography–This test helps to assess the stiffness of the liver and how severe the scarring is in the child’s liver.
- Body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) – This test is performed to evaluate the biliary system that is part of the liver.
- Biopsy – With the part of the liver tissue sample, in this test, the doctor analyzes the extent of the liver damage.
- Liver function test – In the liver function test, a doctor examines blood for particular enzymes that signal that liver damage is present.
Treatment: Home Care, Medications, and Surgery
Treatment of pediatric cirrhosis depends on how badly the liver is injured. The ultimate goal is to protect the healthy tissue a child has left. As a first step, a doctor may suggest some lifestyle changes, including:
- Diet change, such as a low-sodium or plant-based diet.
- A doctor may recommend losing weight if a child is obese, and cirrhosis is because of fat buildup in his/her liver.
Medications
A doctor may prescribe some medicines to avoid infections and reduce toxins in the blood. A doctor may even suggest some vaccinations for viral hepatitis, pneumonia, and influenza to help a child avoid potential illnesses that can cause infections.
Surgery
In severe conditions, a pediatric liver transplant may be needed to replace the damaged liver with a healthy one from a donor.
Precautions
Pediatric cirrhosis is usually not preventable, but one can take precautions for it. Ensure a child receives proper vaccinations and medications. A healthy lifestyle and balanced nutrition intake is a crucial part of preventing cirrhosis of the liver in children.
Wrapping Up
To sum it all up, the better parents take care of a kids’liver, the better it will take care of them. The liver works very hard to keep a person healthy. Therefore, a person can help it by eating healthy – well-balanced food, drinking water, and exercising regularly to keep body systems working well. Therefore, parents should make their children understand the importance of taking a nutritious diet and regular exercise.
Mostly overconsumption of alcohol is the main reason for cirrhosis in adults. There should be no amount of alcohol consumption by either parent even during pregnancy is advisable because it can cause pediatric cirrhosis.
 Donate
now
Donate
now


Related Posts
Aayush Jadav- A Remarkable Journey of Hope
moreKaivalya Mayane- A Remarkable Journey of Hope
moreVendant Joshi- A Remarkable Recovery
more